The Webb Space Telescope is so cool and strong. And while its unmatched capabilities are teaching us new things about our universe, it's also really, really good for taking better pictures of things we already know about. When you get a fancy new phone with a superior camera, do you decline to take new pictures of your cat because you've already got hundreds? You do not. And so this year Webb turned its Mid-InfraRed Instrument on the Whirlpool Galaxy, already one of the most well-known, -studied, and -photographed galaxies there is, just to see what this baby could do. And it was good—as someone or other once said.
No need to wonder why Messier 51a is nicknamed the Whirlpool Galaxy: Stare deeply into its core, its compact dust clouds lit up pale blue and bright white with the reflection of the countless ancient starts within, and you feel like you're falling down, down, down along its sharply defined spiral arms, which swirl hypnotically and inexorably through the eons and kiloparsecs. The arms are themselves set off by brighter regions, where newborn stars are being formed, and darker, less active ones, and black spaces between the filaments which are truly empty for light years around. Everything here is happening at scales it's hard to comprehend—the galaxy itself is about 109,000 light years across—but training the JWST on it illuminates the smaller-scope structures in ways new to science and pleasing to the eye.
And it is a crowd-pleaser: This image was selected by the public as the top Webb image of 2023, which is the flimsy-as-hell news peg I'm using to blog about it now, with a full-bleed picture and with zero regrets. This image beat out some real stunners—the candy-colored supernova shell Cassiopeia A is a highlight—but it's hard to top this for its ability to capture and awe.
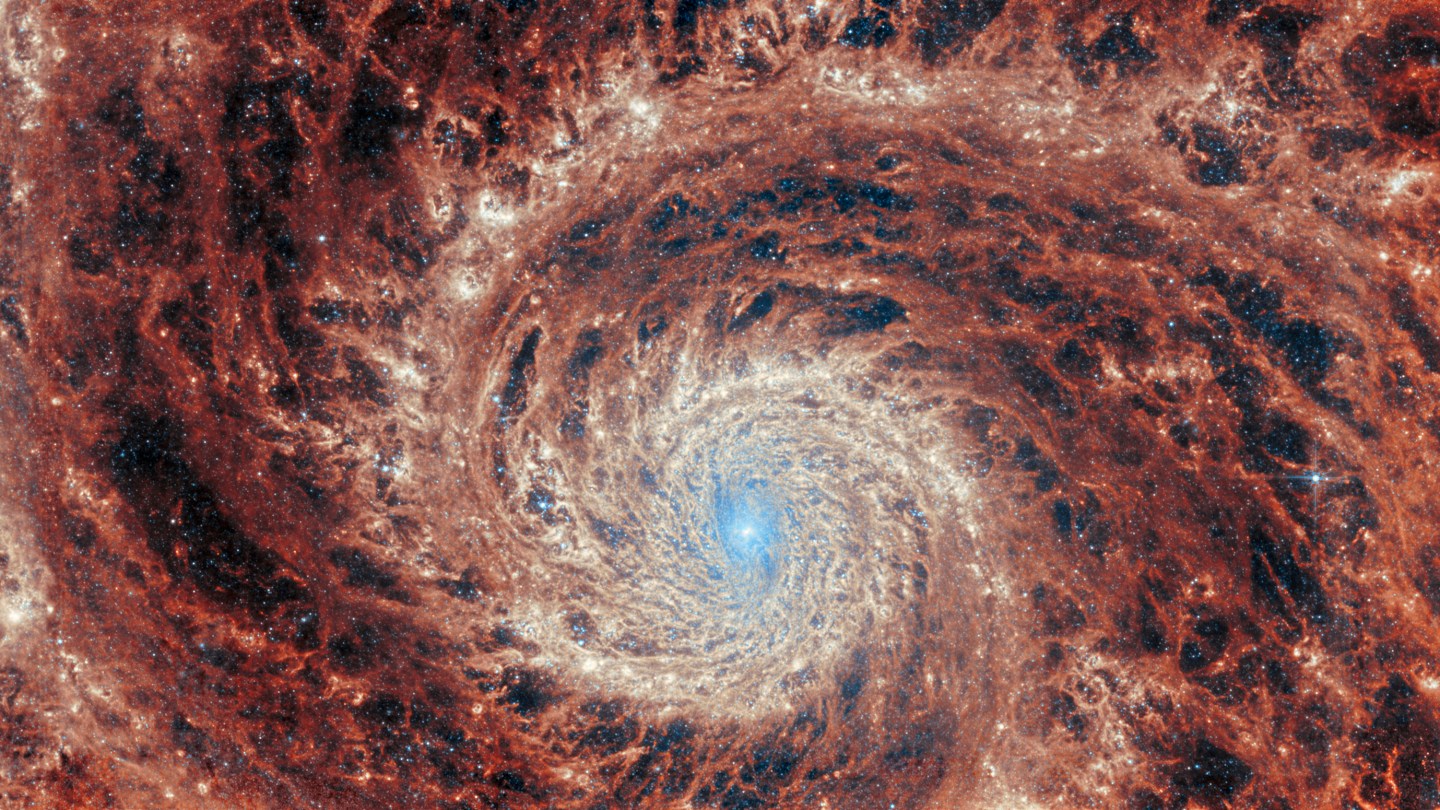
The Whirlpool Galaxy is something of a star among amateur astronomers. Its orientation (just about head-on to Earth) and relative proximity (a mere 32 million light years) made it easily resolvable by basic backyard telescopes, and under certain conditions it's even viewable through binoculars. It's one of the earliest intergalactic objects to be cataloged, as is evident in its low Messier number, and was the first "nebula"—this was back when we didn't really understand what galaxies were—to be known to have a spiral shape. Consider Lord Rosse's 1845 drawing, as viewed through his telescope the Leviathan of Parsons, and the famous Hubble Image, and now, the Webb; we've known since pretty early on what it looks like, and what it looks like is something we can't turn our eyes away from.
Part of the appeal is companion galaxy NGC 5195, which appears to be sucking down one of the Whirlpool Galaxy's spiral arms. This is something of an optical illusion—the companion is actually well behind the Whirlpool, from our perspective—but the two are influencing each other. They are connected by a tidal bridge of dust backlit by NGC 5195, and the smaller galaxy is exerting complex but important gravitational effects on the larger. NGC 5195's gravity as it passes to and fro around the Whirlpool squeezes and pulls its spiral arms, creating denser areas of dust on the arms' inner edges, which make for especially rich star-forming regions. Eventually, those new stars clear their neighborhoods with their stellar winds or by going supernova, sweeping the dust away and leaving the dark patches between the filaments that we see today.
We know about the mechanics of star formation, especially in galaxies not our own, only in the broadest strokes. In that sense, Webb's contribution to science will be iterative, its unparalleled clarity letting us see old things in newer ways and on more finely grained scales, and work out slightly more accurately what's going on out there. That when translated visually this data-gathering presents as something that strikes the aesthetic part of the human soul—that's just a happy accident of the universe.
![The graceful winding arms of the grand-design spiral galaxy M51 stretch across this image from the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope. Unlike the menagerie of weird and wonderful spiral galaxies with ragged or disrupted spiral arms, grand-design spiral galaxies boast prominent, well-developed spiral arms like the ones showcased in this image. This galactic portrait was captured by Webb’s Mid-InfraRed Instrument (MIRI). In this image the reprocessed stellar light by dust grains and molecules in the medium of the galaxy illuminate a dramatic filamentary medium. Empty cavities and bright filaments alternate and give the impression of ripples propagating from the spiral arms. The yellow compact regions indicate the newly formed star clusters in the galaxy. M51 — also known as NGC 5194 — lies about 27 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation Canes Venatici, and is trapped in a tumultuous relationship with its near neighbour, the dwarf galaxy NGC 5195. The interaction between these two galaxies has made these galactic neighbours one of the better-studied galaxy pairs in the night sky. The gravitational influence of M51’s smaller companion is thought to be partially responsible for the stately nature of the galaxy’s prominent and distinct spiral arms. If you would like to learn more about this squabbling pair of galactic neighbours, you can explore earlier observations of M51 by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope here. This Webb observation of M51 is one of a series of observations collectively titled Feedback in Emerging extrAgalactic Star clusTers, or FEAST. The FEAST observations were designed to shed light on the interplay between stellar feedback and star formation in environments outside of our own galaxy, the Milky Way. Stellar feedback is the term used to describe the outpouring of energy from stars into the environments which form them, and is a crucial process in determining the rates at which stars form. Understanding stellar feedback is vital to building accurate universal models of star formation. The aim of the FEAST observations is to discover and study stellar nurseries in galaxies beyond our own Milky Way. Before Webb became operative, other observatories such as the Atacama Large Millimetre Array in the Chilean desert and Hubble have given us a glimpse of star formation either at the onset (tracing the dense gas and dust clouds where stars will form) or after the stars have destroyed with their energy their natal gas and dust clouds. Webb is opening a new window into the early stages of star formation and stellar light, as well as the energy reprocessing of gas and dust. Scientists are seeing star clusters emerging from their natal cloud in galaxies beyond our local group for the first time. They will also be able to measure how long it takes for these stars to pollute with newly formed metals and to clean out the gas (these time scales are different from galaxy to galaxy). By studying these processes, we will better understand how the star formation cycle and metal enrichment are regulated within galaxies as well as what are the time scales for planets and brown dwarfs to form. Once dust and gas is removed from the newly formed stars, there is no material left to form planets. [Image Description: A large spiral galaxy takes up the entirety of the image. The core is mostly bright white, but there are also swirling, detailed structures that resemble water circling a drain. There is white and pale blue light that emanates from stars and dust at the core’s centre, but it is tightly limited to the core. The detailed rings feature bands of deep orange and cloudy grey, which are interspersed by darker empty regions throughout.]](https://lede-admin.defector.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/28/2023/12/potm2308c.jpg?w=2880)





